Parameterized Reports
Overview
R Markdown documents can optionally include one or more parameters. Parameters are useful when you want to re-render the same report with distinct values for various key inputs, for example:
Running a report specific to a department or geographic region.
Running a report that covers a specific period in time.
Running multiple versions of a report for distinct sets of core assumptions.
R Markdown parameter names, types, and default values are declared in the YAML section at the top of the document. To change these values for a given rendering you use the params argument to the rmarkdown::render function.
Note that parameterized reports are a new feature of R Markdown and therefore require very recent versions of the knitr (v1.11) and rmarkdown (v0.8) packages. You can install the most up to date versions with the following command:
install.packages(c("knitr", "rmarkdown"))Declaring Parameters
YAML Params Field
Parameters are declared using the params field within the YAML section at the top of the document, for example:
---
title: My Document
output: html_document
params:
region: east
---Parameter values can be provided inline as illustrated above or can be included in a value sub-key. For example:
---
title: My Document
output: html_document
params:
region:
value: east
---This second form is useful when you need to provide additional details about the parameter (e.g. information about how parameters should be presented to end-users).
Parameter Types
All of the standard R types that can be parsed by the yaml::yaml.load function are supported including character, integer, numeric, and logical. In addition, you can use arbitrary other R object types by specifying the value using an R expression. For example, to specify a date or date-time you could use this code:
---
title: My Document
output: html_document
params:
start: !r as.Date("2015-01-01")
snapshot: !r as.POSIXct("2015-01-01 12:30:00")
---Note that the date and data-time values are prefaced with !r, which indicates that the value is an R expression rather than a literal value.
Using Parameters
Accessing from R
The declared parameters are automatically made available within the knit environment as components of a read-only list named params. For example, the values of the above two parameters can be accessed in a chunk with the following R code:
```{r}
params$region
params$start
```When you preview the document in RStudio (or otherwise call the rmarkdown::render function with no arguments) the default parameter values listed in the YAML will be used.
Passing Parameters
To vary the parameters of an R Markdown document from the defaults you use the params argument of the rmarkdown::render function. For example:
rmarkdown::render("MyDocument.Rmd", params = list(
region = "west",
start = as.Date("2015-02-01")
))You can of course specify only a subset of the available parameters in your call to render. For example:
rmarkdown::render("MyDocument.Rmd", params = list(
region = "west"
))In this case the default values are used for any parameters not explicitly provided.
You might also find it convenient to wrap the call to render in an R function, for example:
renderMyDocument <- function(region, start) {
rmarkdown::render("MyDocument.Rmd", params = list(
region = region,
start = start
))
}Parameter User Interfaces
In the Passing Parameters section above we described wrapping the invocation of a report in an R funtion to allow customization of it’s parameters. It’s also possible to provide a user-interface for specifying parameter values.
If your document contains parameters and you specify the params = "ask" argument to the render function then a user-interface is provided to specify the parameter values. For example, consider the following parameter declarations:
---
title: "My Document"
output: html_document
params:
minimum: 100
region: east
data: results.csv
---If you call the render function as follows:
rmarkdown::render("MyDocument.Rmd", params = "ask")Then you’ll see the following user-interface for parameter entry:
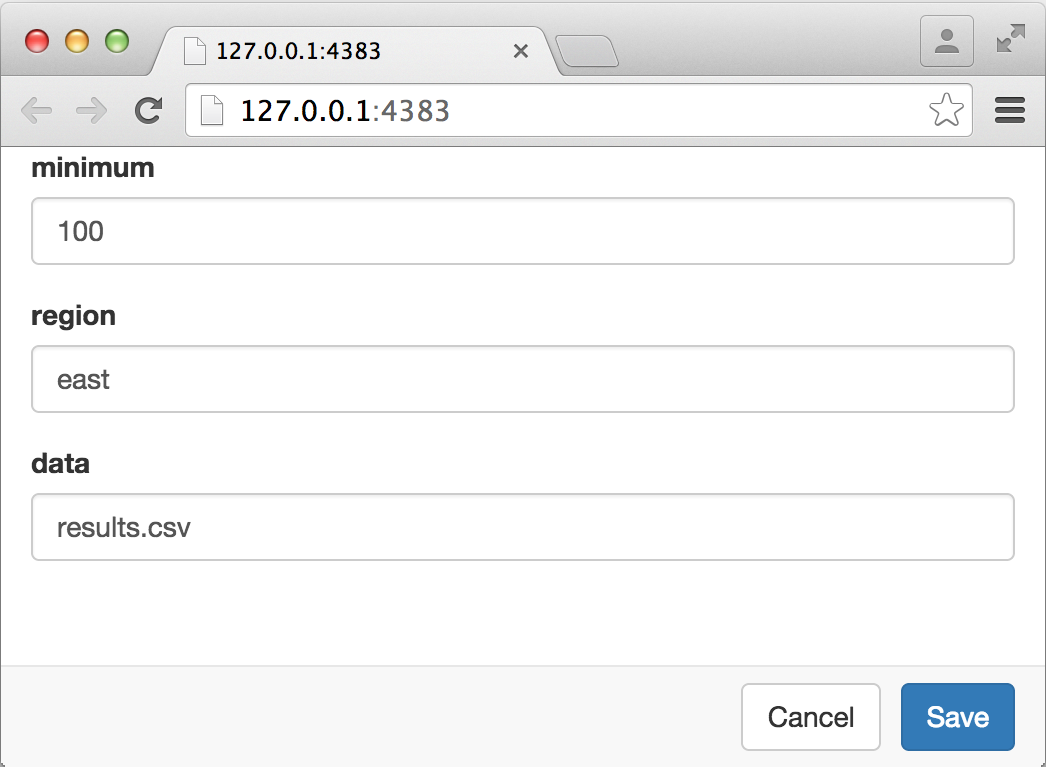
The user-interface is generated using Shiny and as a result can take advantage of standard Shiny input controls. You can customize inputs by adding the appropriate values to the parameter YAML. For example, the following parameters are customized to use the Shiny sliderInput, selectInput, and fileInput controls:
---
title: "My Document"
output: html_document
params:
minimum:
label: "Minimum:"
value: 100
input: slider
min: 0
max: 1000
region:
label: "Region:"
value: east
input: select
choices: [east, west, north, south]
data:
label: "Input dataset:"
value: results.csv
input: file
---This results in the following user-interface for parameter editing:
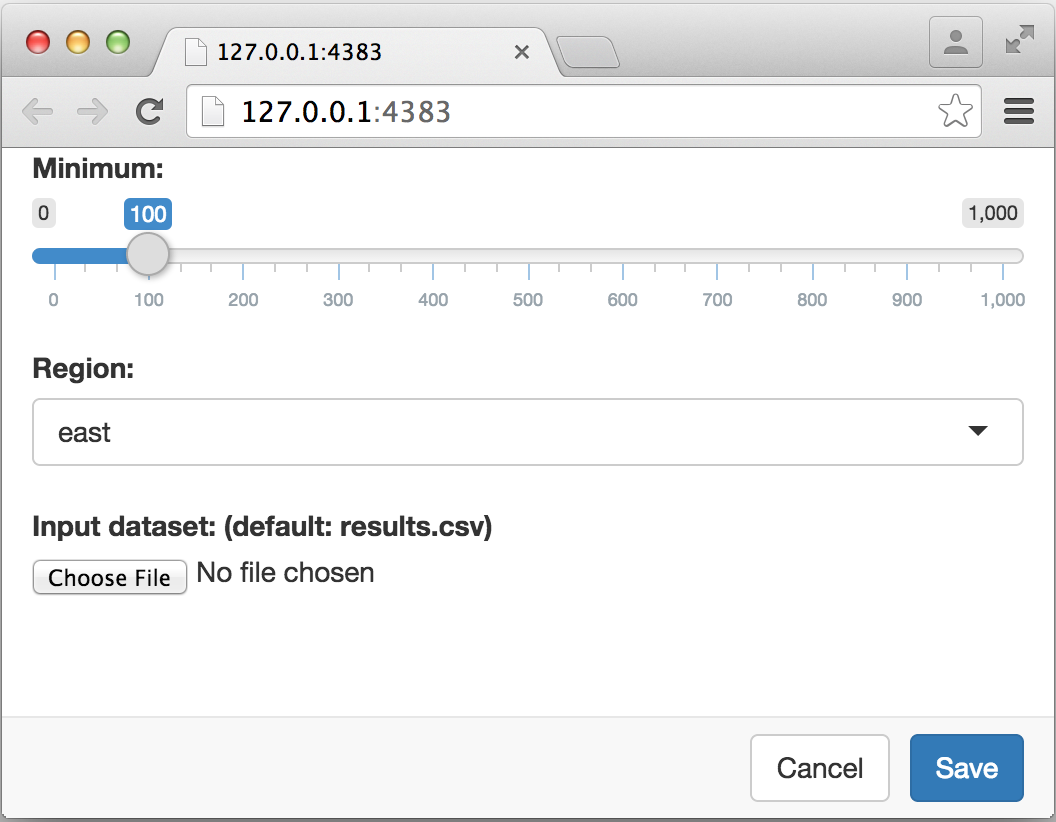
The type of Shiny control used is controlled by the input field. The following input types are currently supported (see the help for the associated Shiny function for additional attributes which can be specified to customize the input):
| Input Type | Shiny Function |
|---|---|
| checkbox | checkboxInput |
| numeric | numericInput |
| slider | sliderInput |
| date | dateInput |
| text | textInput |
| file | fileInput |
| radio | radioButtons |
| select | selectInput |
| password | passwordInput |
Note that attributes provided for parameters are automatically passed as arguments to the respective Shiny input functions listed above.
RStudio Preview
When previewing an R Markdown document within RStudio you can use the Knit with Parameters command (available from the standard Knit toolbar menu) to specify parameters prior to previewing.